-
Quantum Dot
A quantum dot solar cell is a solar cell design that uses quantum dots as the absorbing photovoltaic material. It attempts to replace bulk materials such as silicon, copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) or CdTe. Quantum dots have bandgaps that are tunable across a wide range of energy levels by changing the dots' size. In bulk materials the bandgap is fixed by the choice of material(s). This property makes quantum dots attractive for multi-junction solar cells, where a variety of materials are used to improve efficiency by harvesting multiple portions of the solar spectrum.
Perovskite
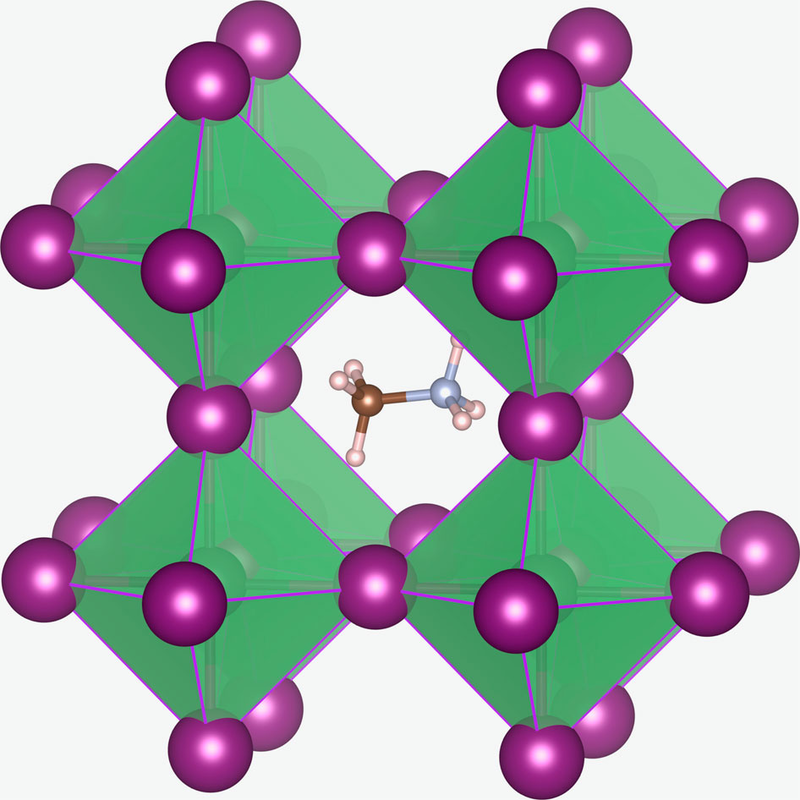
A perovskite solar cell is a type of solar cell which includes a perovskite structured compound, most commonly a hybrid organic-inorganic lead or tin halide-based material, as the light-harvesting active layer.[1] Perovskite materials such as methylammonium lead halides are cheap to produce and simple to manufacture.